Glossary-Test
Adipose
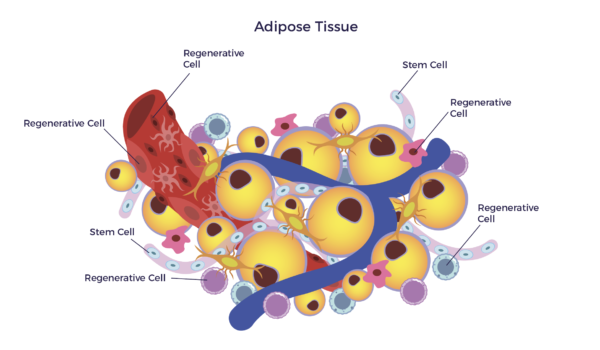
The medical term for fat. Fat cells group to comprise fat tissue which is found below the skin and around internal organs. These groupings of fat cells act as a storage tank of usable energy and a cushion to the body.
Adipose Derived Regenerative Cells (ADRCs)
A mixed population of stem cells and regenerative cell types which participate in the repair, growth and regeneration of damage within the body.
Ambrose
From the Latin Ambrosius, Greek Ambrosios, meaning ‘immortal, belonging to the immortals.’
Amplification Loop
The perpetuation of exaggerated cell death and inflammation, which is due to stimulation of the same cell or nearby cells.
Angiogenesis
The formation of new blood vessels.
Apoptosis
The process of cell death.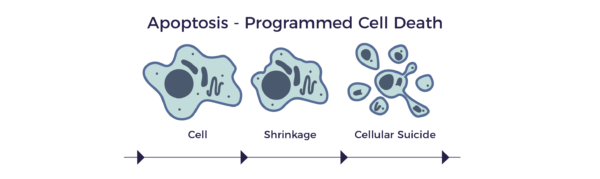
Autocrine Signal
A chemical messenger that is released by a cell, which is reacted to by the same cell.
Autoimmune
Relating to the body’s defensive response in which lymphocytes and antibodies attack substances in the body.
Autologous
Belonging to the same organism. Your own.
Bioactive
Having an effect, a response or an interaction with a living tissue.
Blood Brain Barrier
An important mechanism of protecting the brain. This is carried out by capillaries (very fine blood vessels) that carry blood to the brain and spinal cord which tightly regulate and filter the passing of certain substances.
Bone Marrow
Spongy tissue inside bones, including the hip and thigh bones, in which blood cells are made.
Bursa
Fluid filled sac that cushions joint movement.
Cell
The smallest living structure capable of independent existence. Cells are specialized in both their structure and their function. A group of cells form an organ or tissue.
Cell Differentiation
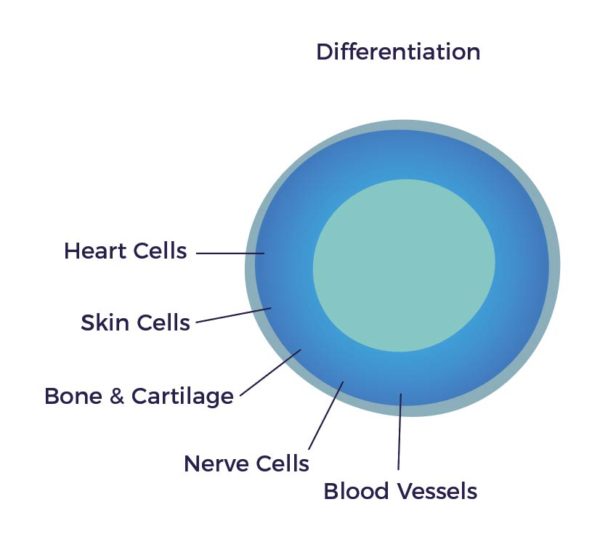
When a cell becomes more specialized and turns into a different cell type. An example of this is a stem cell becoming a nerve cell.
Cell-to-Cell Communication or Signaling (Paracrine Signaling)
Information exchanged by one cell to another cell. This is done by direct contact of the cells, or by release of a substance.
Cell Therapy
At AMBROSE, cell therapy is the utilization of clinical grade adipose-derived stem and regenerative cells (ADRCs) for the potential therapeutic benefits that these cells can offer. ADRCs are known to possess powerful capabilities of repair including decreased inflammation, modulation of overactive immune cells, the promotion of new blood vessel growth, prevention of cell death, decreased scar tissue and, finally, the regeneration of new, healthy tissue.
Charlie’s Law
Texas House Bill 810, also known as Charlie’s Law, allows the use of investigational adult stem cell treatments in Texas for patients that have been diagnosed with a terminal illness or severe chronic disease. This law is known as a “Right to Try” law.
Chronic Disease
A disease or condition that persists for a long time (usually at least a year) which require ongoing medical care and limit activities of daily living (ADLs).
Clinical Trial
A research study in which a human is assigned to a treatment to evaluate its effects on health.
C-Reactive Protein (CRP)
A blood marker of inflammation that is not found when one is in a healthy state. CRP appears after an injury, infection or inflammation and disappears when the abnormality is resolved. Elevated levels of CRP can suggest a higher risk of heart disease, stroke, hypertension and diabetes.
Cytokine
A protein molecule that regulates the intensity and duration of an immune response.
