Ambrose Treatment Summary Glossary
Spine
Spine Injections
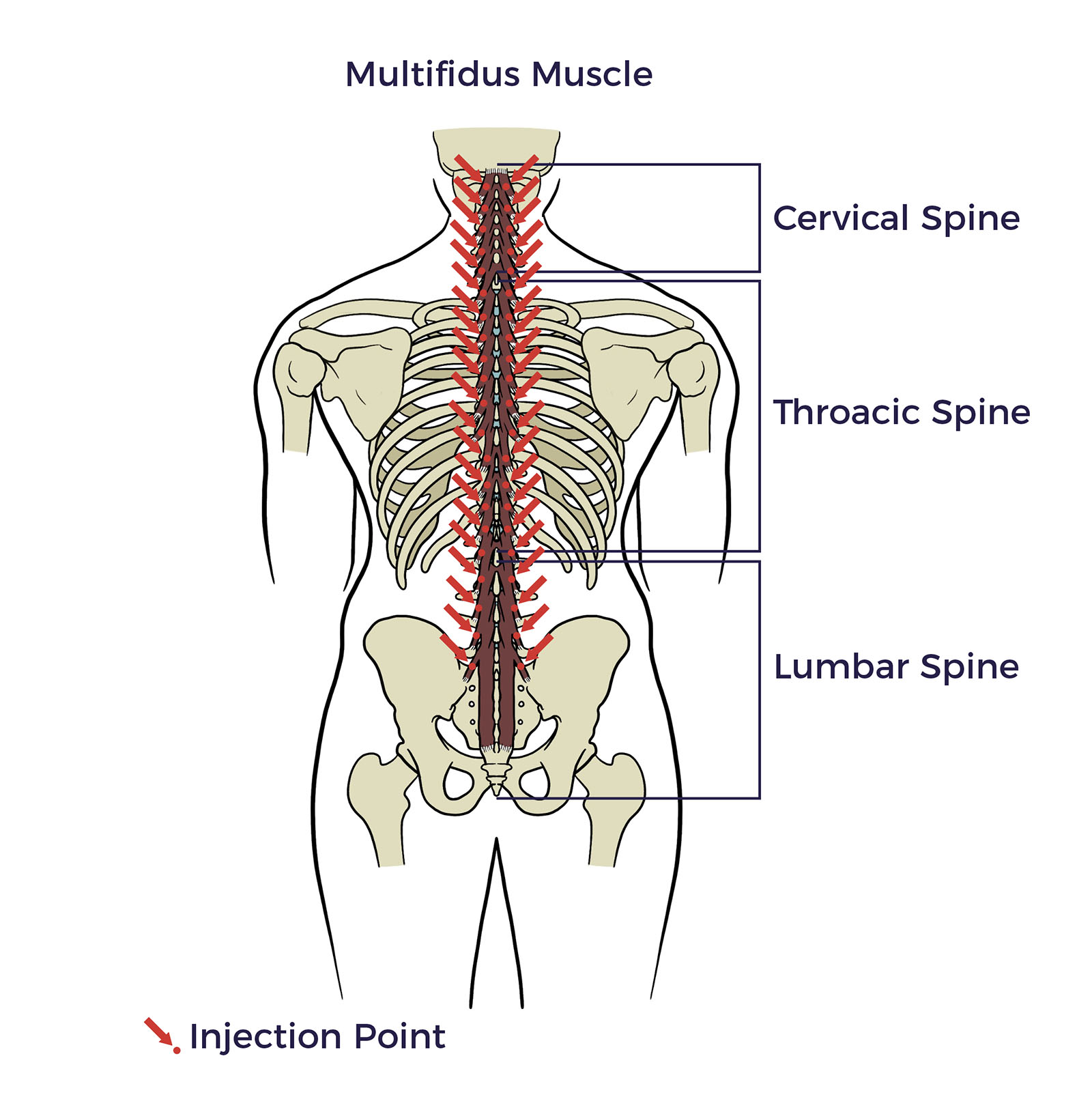
Multifidus Muscle
The multifidus muscle is a deep spinal muscle located along both sides of the spine, playing a crucial role in spinal stability and movement.
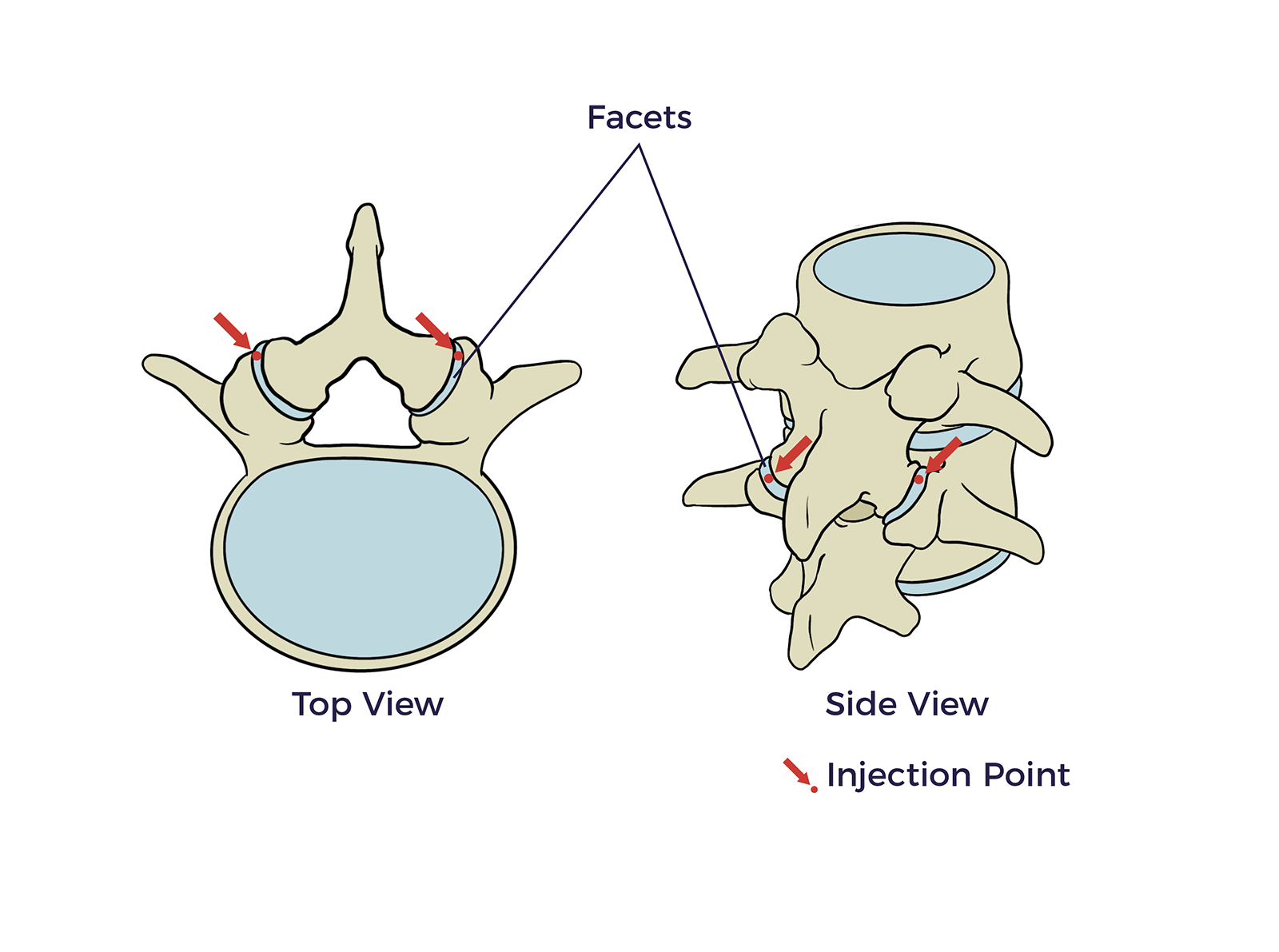
Facets
Facet joints are pairs of small joints in between the vertebrae in the back of the spine; your
injections are received in the para facets.
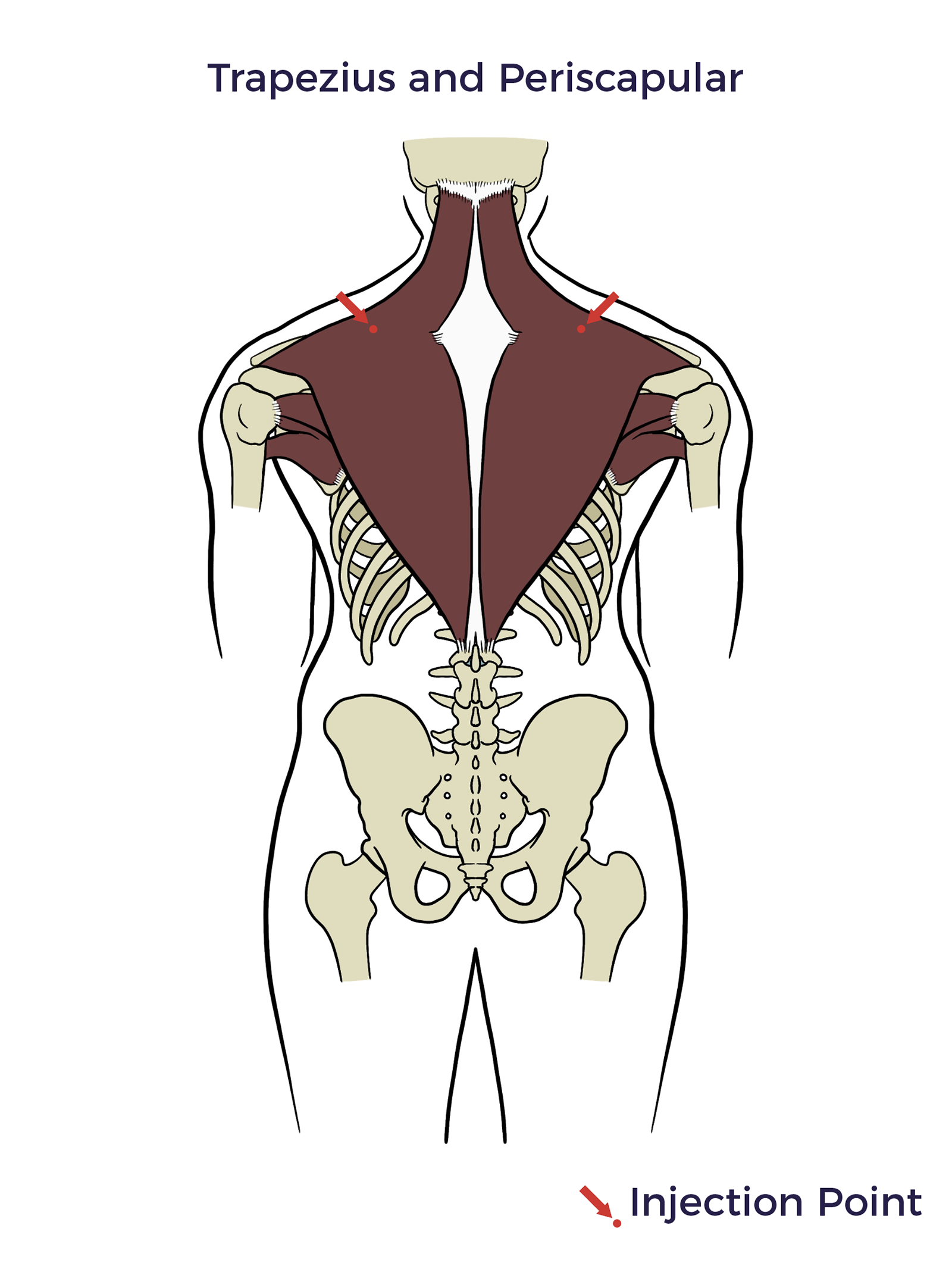
Shoulders
Trapezius and Periscapular
The trapezius muscle is a large superficial back muscle. The periscapular refers to the area around the shoulder blade.
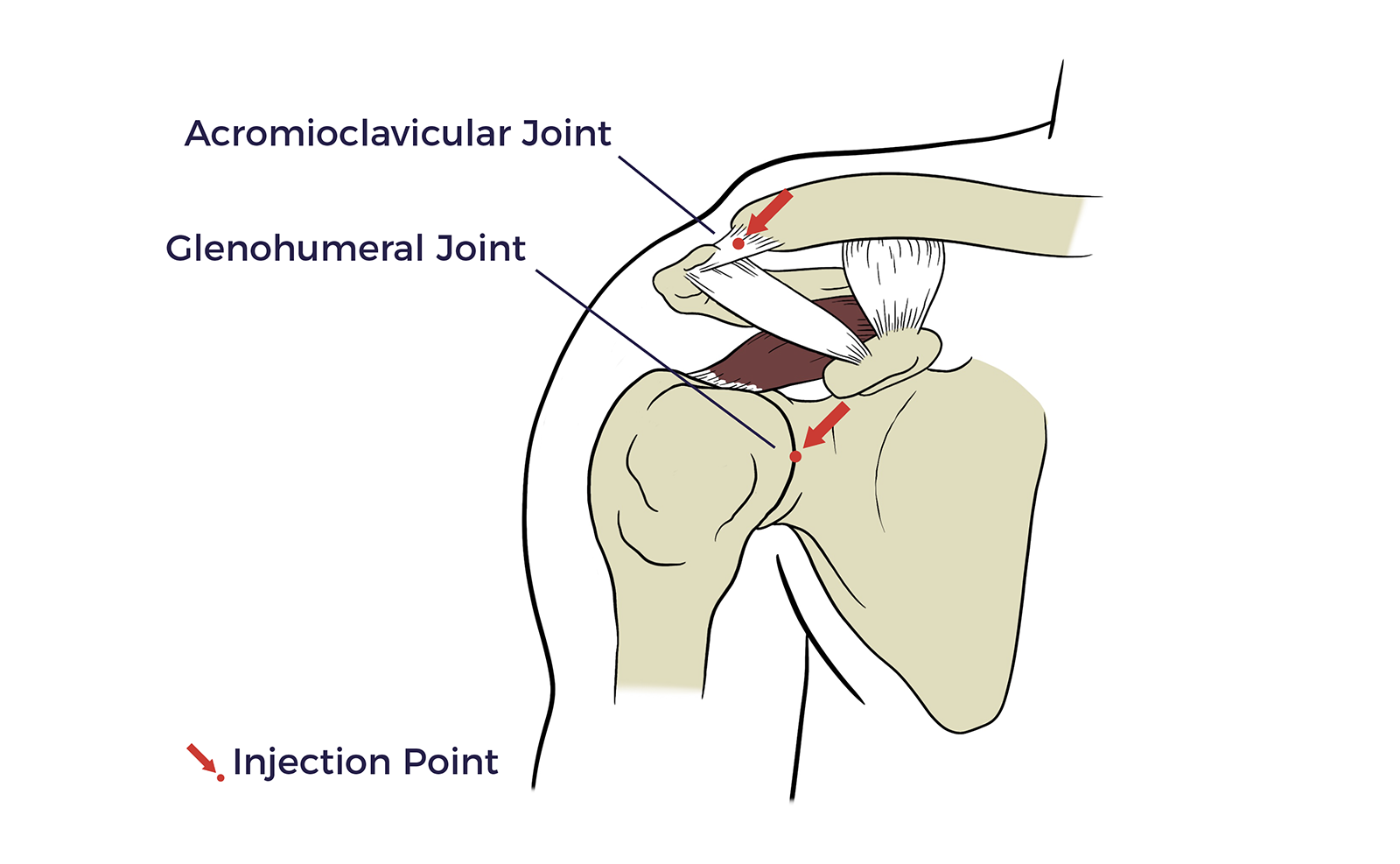
Acromioclavicular Region
The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is formed by the cap of the shoulder and the collar bone.
Glenohumeral Joint
The glenohumeral joint, also known as the shoulder joint, is a ball-and-socket joint where the rounded end of the upper arm bone fits into a shallow socket on the shoulder blade.
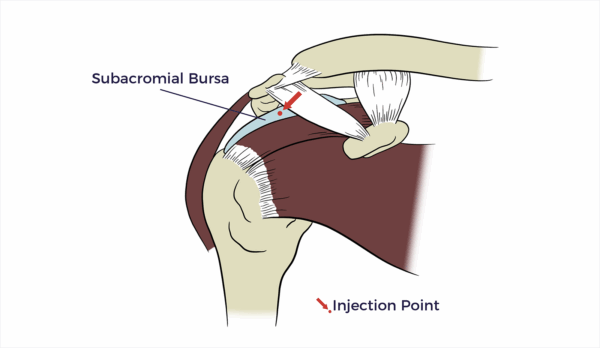
Subacromial Bursa
The subacromial bursa is a fluid-filled sac located in the shoulder joint.
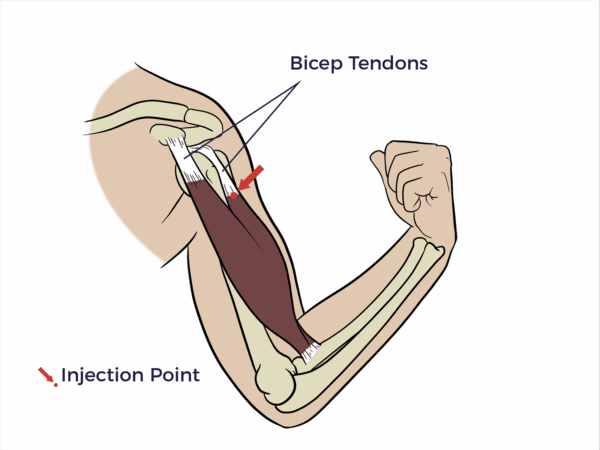
Biceps Tendon
The biceps tendon is a strong, cord-like structure that connects the biceps muscle to bones, specifically the shoulder and elbow.
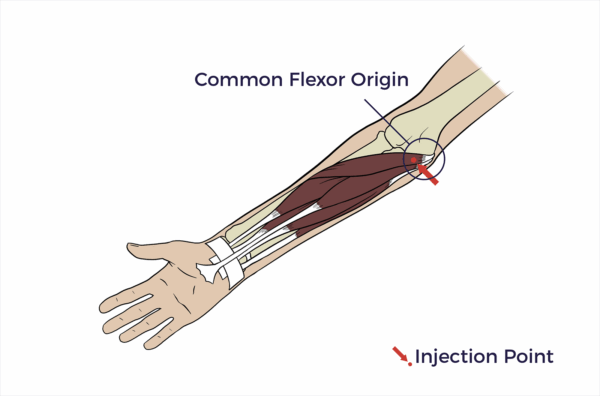
Elbow
Common Flexor Origin at Humeral Medial Epicondyle
The “common flexor origin at the humeral medial epicondyle” refers to a single tendon where several forearm flexor muscles originate.
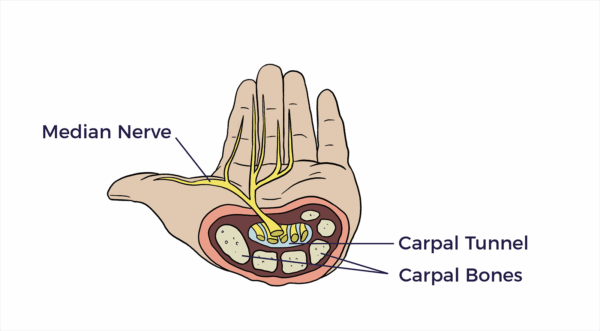
Wrist
Median Nerve/Carpal Tunnel
The carpal tunnel is a passageway in the wrist, formed by bones and a ligament, that houses the median nerve and tendons.
Hands
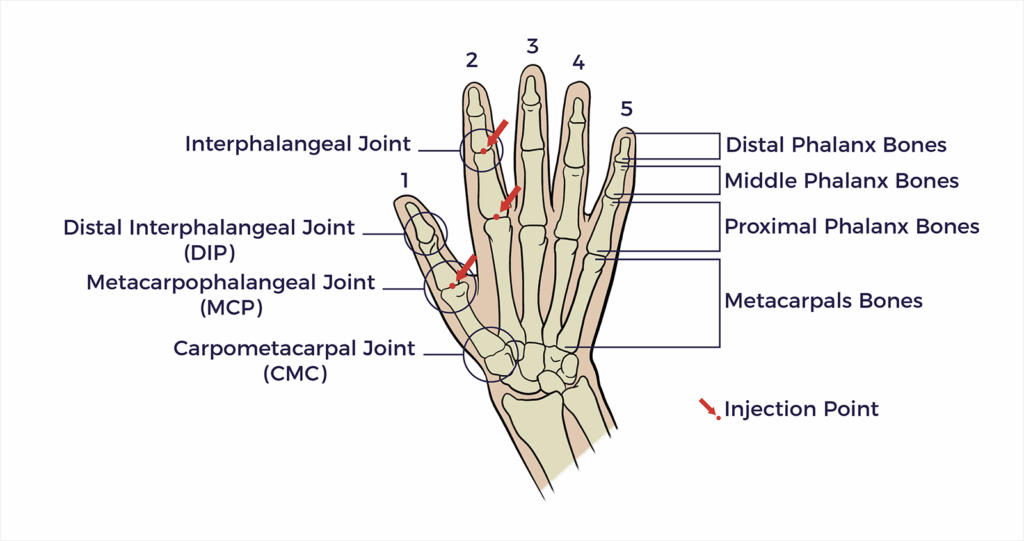
1st Interphalangeal Joint
The 1st interphalangeal joint is the hinge joint between the first two bones of a finger. It allows for bending and straightening of the finger.
2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th Distal Interphalangeal Joints
The 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and 5th distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints are the joints located at the tips of the fingers.
1st Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) Joint
The 1st metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint is the thumb’s joint.
1st Carpometacarpal (CMC) Joint
The 1st carpometacarpal (CMC) joint, also known as the thumb’s basal joint, is a saddleshaped joint located at the base of the thumb, where it connects to the hand.
Hips and Pelvis
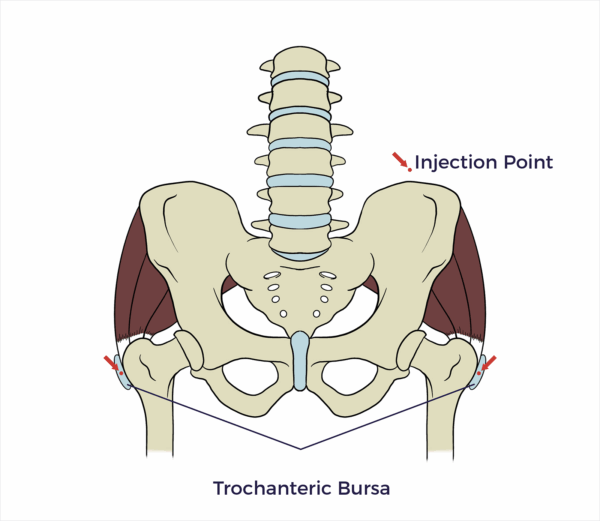
Trochanteric Bursa
The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac located on the lateral (outside) aspect of the hip, near the greater trochanter.
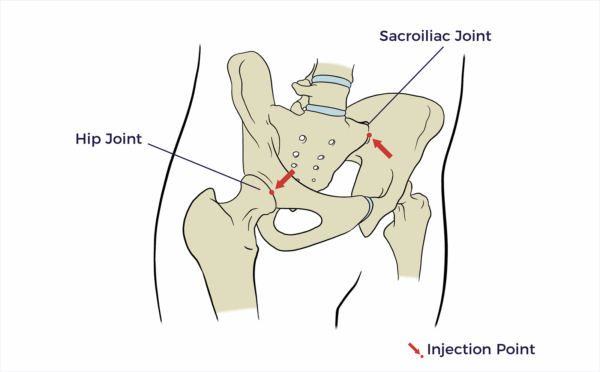
Hip Joint/Intra-Articular
An intra-articular hip injection involves injecting directly into the hip joint to relieve pain and inflammation.
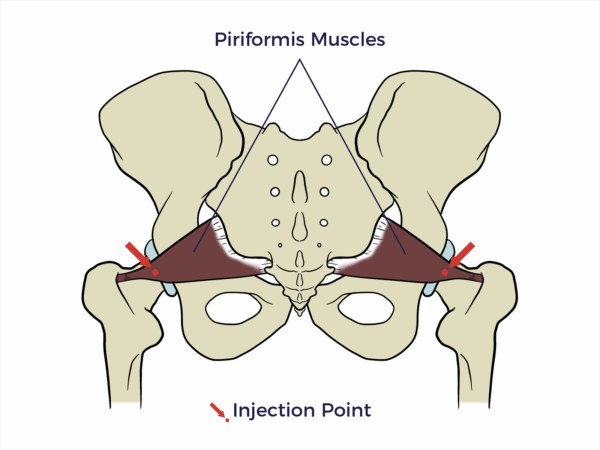
Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle is a pear-shaped muscle located deep in the buttock, between the sacrum and the femur.
Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is located at the base of the pelvis.
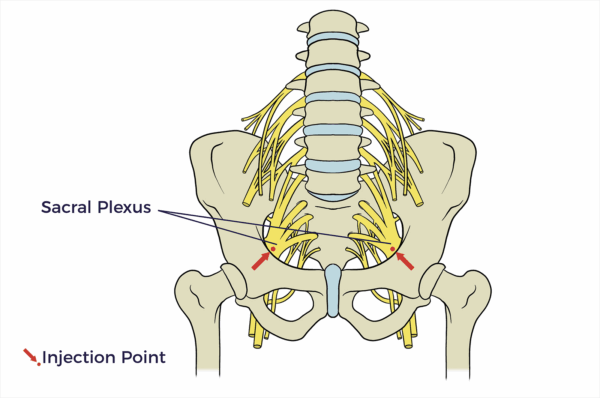
Sacral Plexus
The sacral plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and muscles of the pelvis and lower limb.
Legs
Iliotibial Band
The iliotibial band (IT band) is a thick band of fibrous tissue that runs along the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee.
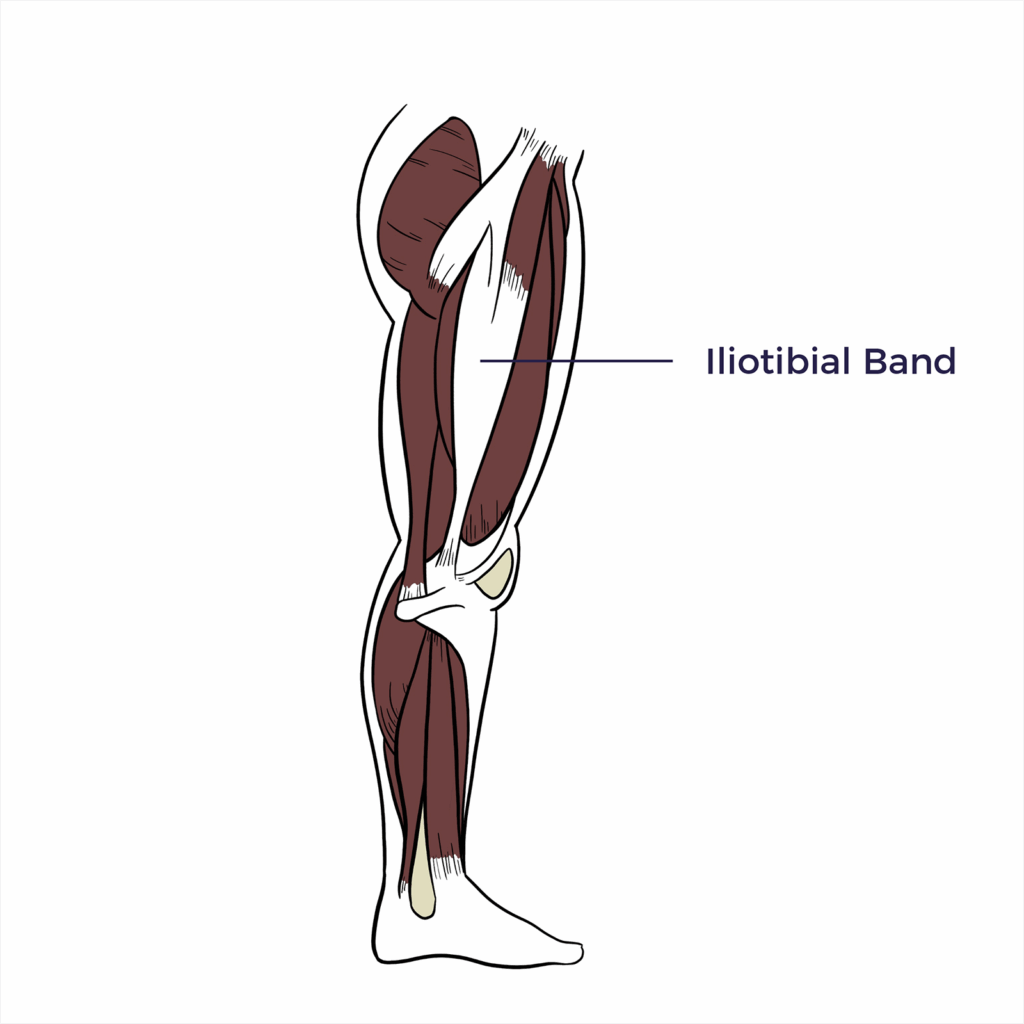
Iliotibial Tendon
The iliotibial band (IT band) is a thick band of connective tissue, also known as a tendon, that runs along the outside of the thigh, from the hip to the knee.
Knees
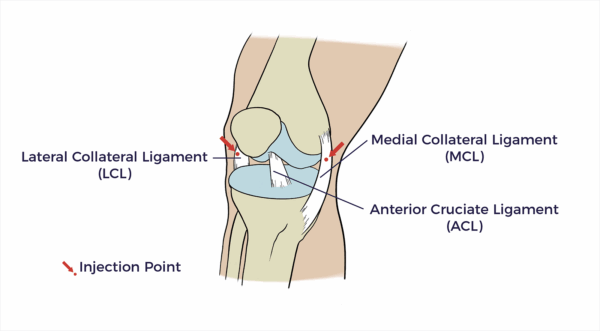
Medial Collateral Ligament Region
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat, band-like connective tissue located on the inner side of the knee joint.
Lateral Collateral Ligament Region
The lateral collateral ligament region is a band of tissue on the outside of the knee joint.
Patellar Tendon
The patellar tendon attaches the bottom of the kneecap to the top of the shinbone.
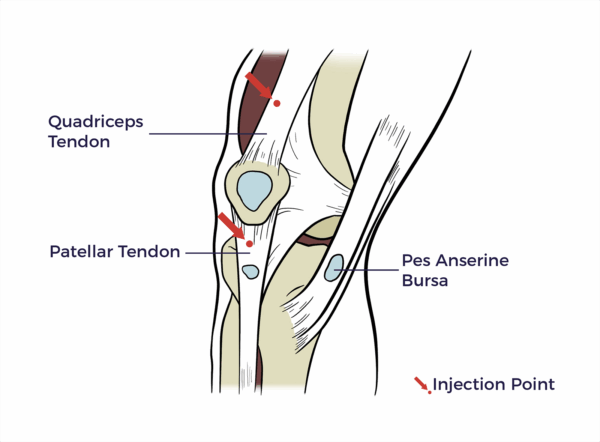
Pes Anserine Bursa
The pes anserine bursa is a fluid-filled sac located on the inner side of the knee, just below the knee joint.
Quadriceps Tendon
The quadriceps tendon is a thick, fibrous tissue located at the top of the kneecap (patella).
Feet and Ankles
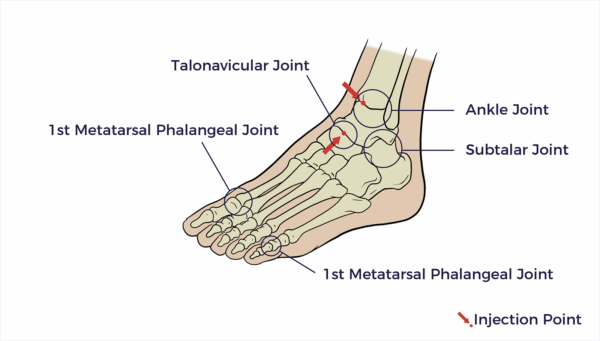
1st Metatarsal Phalangeal Joint
Metatarsophalangeal or Big Toe Joint. The 1st Metatarsophalangeal joint is located at the base of the big toe. This joint helps with toe-off when walking. This is often the site of a bunion or arthritic changes within the joint.
Talonavicular Joint
The talonavicular joint is a part of your foot that connects the ankle bone and the bone in the midfoot.
Subtalar Joint
The subtalar joint is a joint in the foot located below the ankle joint. It allows for side-to-side movements of the foot, which are crucial for balance and adapting to uneven surfaces.
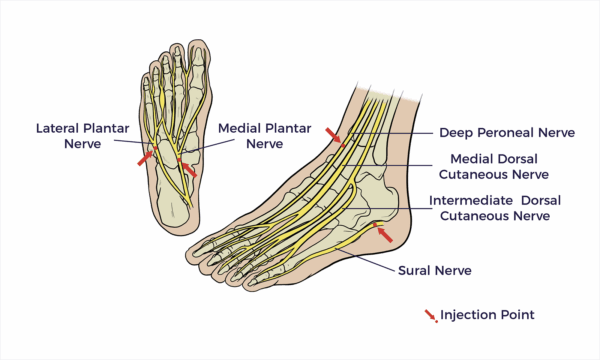
Medial and Lateral Plantar Nerve
The medial and lateral plantar nerves provide both motor and sensory supply to the sole of the foot.
Deep Peroneal Nerve
Provides motor function to the muscles in the front of the leg and the top of the foot, and sensory function to the skin between the first and second toes.
Medial Dorsal Cutaneous Nerve
The medial dorsal cutaneous nerve is a sensory nerve in the foot. It’s a branch of the peroneal nerve and provides sensation to the skin on the inside of the top of the foot.
Sural Nerve
The sural nerve is a sensory nerve in your lower leg that provides feeling to the outer part of your ankle, heel, and foot.
Deltoid Ligament
The deltoid ligament is a strong, triangle-shaped ligament on the inner side of the ankle.
Posterior Tibial Tendon
The posterior tibial tendon is a strong band of tissue that connects the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot.
Plantar Fascia
The plantar fascia is a thick band of tissue on the bottom of your foot that supports your arch and acts as a shock absorber.
Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon is a strong, thick tendon at the back of your ankle that connects your calf muscles to your heel bone.
